Non-Intrusive DAS Coexisting in Telecom Networks
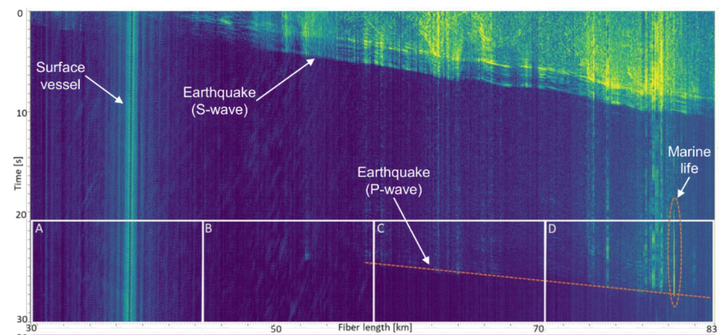 Illustration of environmental signals captured by DAS with data traffic on a telecom fiber optic cable.
Illustration of environmental signals captured by DAS with data traffic on a telecom fiber optic cable.
Abstract
This work presents a method for operating Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) non-intrusively on live telecommunication networks. By using a specific optical channel outside the data transmission bands, we demonstrate that it is possible to perform continuous environmental and geophysical monitoring without affecting the quality of service for telecom data, opening up vast existing fiber networks for scientific sensing.
This paper details a technique to use Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) on fiber optic cables that are simultaneously carrying live telecom data. The key challenge is to avoid interference between the sensing signals and the data channels. Our approach uses a dedicated wavelength for the DAS interrogator that is outside the standard telecom C-band, allowing both systems to operate in parallel on the same fiber.
This non-intrusive method unlocks the potential to use the vast global network of existing subsea and terrestrial telecom cables as dense arrays of environmental sensors for monitoring earthquakes, ocean dynamics, and more.